Fluctuations in Employment and Output Result From Changes in
A Prices are sticky in the short run. In recessions employment falls and un-employment rises.

Introducing Aggregate Demand And Aggregate Supply Boundless Economics
Richter and Nathaniel A.
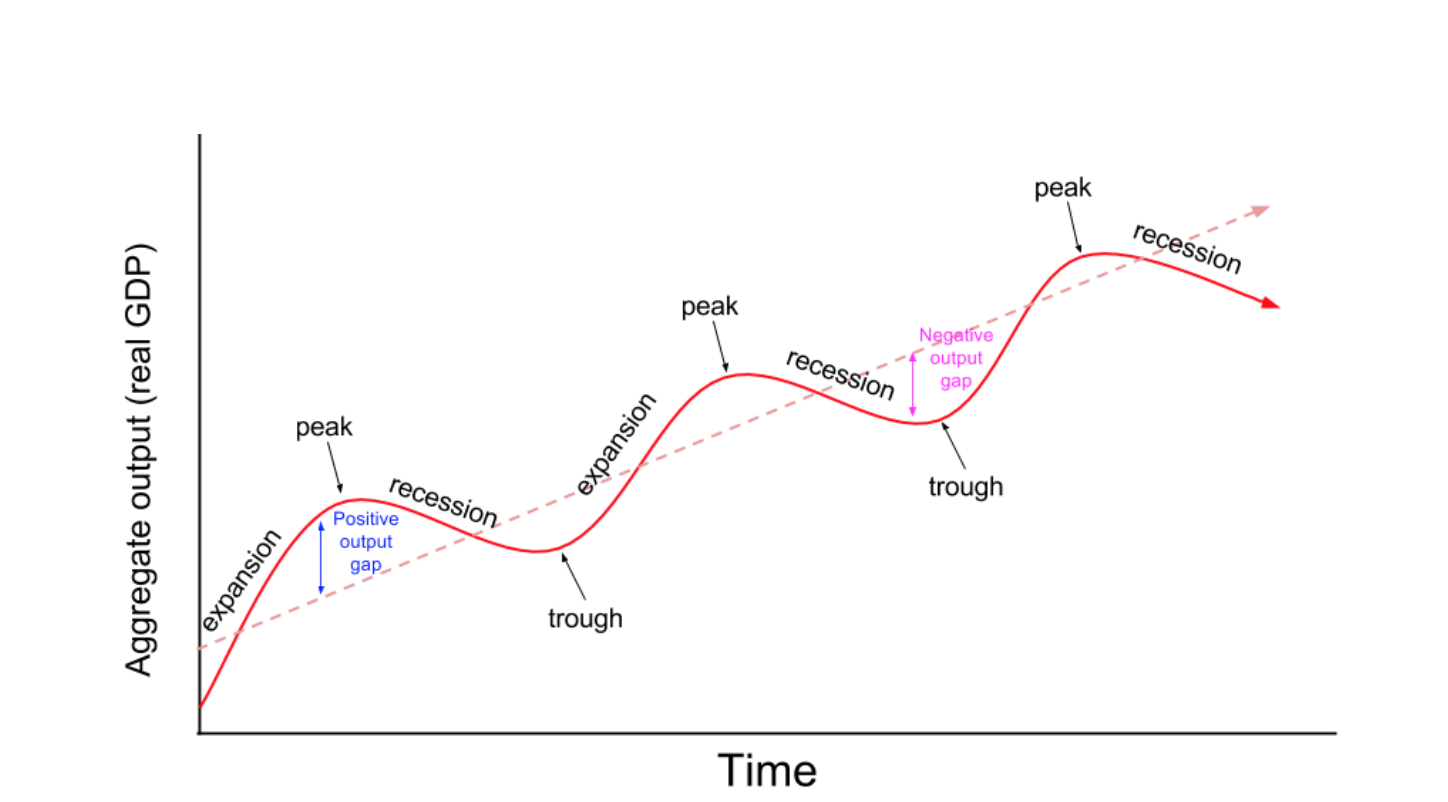
. C Aggregate demand and aggregate supply. Real-business-cycle theory assumes that fluctuations in employment reflect changes. In the years immediately after a recession the labor market is slackÑ unemployment remains high and the vacancy rate and other measures of employer recruiting effort are abnormally low.
Accommodated in one period at the regional level. CUANDO LA PRODUCCIÓN SUBE DE 1 EL EMPLEO DISMINUYE DE 038 Okuns law does not always hold perfectly. And sticky prices are responsible for short-run fluctuations in output and employment.
Economics questions and answers. Aggregate employment is not cyclical in China because the correlation of the aggregate employment and output is close to zero. In the present model fluctuations in hours of work reflect the changing relative labor productivity in home and market activities.
Fluctuations in employment and output result from changes in a. FIRM SIZE DISTRIBUTION AND EMPLOYMENT FLUCTUATIONS. The US has an Okun coefficient of -038 meaning that a 1 increase in the output growth rate decreases employment by 038.
Aggregate demand and aggregate supply. Flexible markets will keep the economy at a full-employment level of spending and output. Thus the inflationary gap occurs when the short-run level of the economy is above the potential GDP which results in upward pressure on prices.
A steady decline in aggregate supply results in stagflation. Unemployment is determined by the rate at which workers lose. And that these fluctuations in technology cause fluctuations in output and employment.
Neither aggregate demand nor aggregate supply. 06-04 Describe why expectations. A consequence of this setup is that real wage fluctuations do not.
What is the primary reason that changes in total spending lead to cyclical changes in output and employment. Only long-run aggregate supply. Aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
B Short-run aggregate supply only. D Long-run aggregate supply. According to Keynes fluctuations in employment and output result from changes in a.
Neither aggregate demand nor aggregate supply. Tion in line with the argument above would make regional output not only. Economic uncertainty varies over time especially during recessions.
Up to 10 cash back Disequilibrium and business cycle analysis and IV. Neither aggregate demand nor aggregate supply. The result is higher output and a higher real interest rate.
ßuctuations in aggregate output and employ-ment. This is about 23 of the. On output and employment.
Okuns coefficient represents how a change in the output growth rate will affect the unemployment rate. Recent research has focused on how changes in uncertainty affect economic activity. Changes in output and employment levels rather than through changes in prices.
This paper proposes to address these issues and solve the question of whether world commodity prices can indeed explain Canadas exchange rate behavior over the last twenty years and whether the Canadian economy is suffering from the Dutch Disease. Predicts that both output and the real wage in logarithms are generated by processes with unit roots while hours of work follow a stationary process. Employment Fluctuation Aggregate Level.
Since unemployment results from the deficiency of aggregate demand employment and income can be increased by increasing aggregate demand. Both households saving activity and firms investment activity are. Due to the increase in aggregate demand corporate profits commodity prices interest rates and inflationary pressures rise.
Fluctuations in employment and output result from changes in. Time series analysis of output and employment. When the available production technology improves the economy produces more output with the same inputs.
THEORY AND EVIDENCE Holger Görg Philipp Henze Viroj Jienwatcharamongkhol Daniel Kopasker Hassan Molana Catia Montagna Fredrik Sjöholm. According to Keynes fluctuations in employment and output result from changes in a. B aggregate supply only.
Once investment increases employment and income increase. This paper studies the effect of the firm-size distribution on the relationship between employment and output. Fluctuations in output have been larger proportionally than fluctuations in the total volume of work measured as employee hours.
D Changes in total spending cause supply shocks that cause cyclical variation. Assuming the propensity to consume to be stable during the short-run aggregate demand can be increased by increasing investment. The Production Process Drives Fluctuations in Output and Uncertainty.
Question 20 025 Points Fluctuations in employment and output result from changes in A aggregate demand only. It presents a fine selection of articles in the growing field ofthe empirical analysis of output and employment fluctuations with applications in a micro-econometric or a time-series framework. In the classical model.
Q rfQt 2 where Qt is national output and q r is output in region r. Oil price changes and its impact on manufacturing employment output and productivity. The paths of these variables have been any-thing but smooth especially during the past decade.
B Prices are flexible in the long run. Chapter 9 Economic Fluctuations and Macroeconomic Theory 10 10. Tyler Atkinson Michael Plante Alexander W.
A more general specifica-. Specification suggests that all the effects of a change in national output are. C Government is unable to respond by changing the amount of money in circulation.
The magnitude of fluctuations in the aggregate employment is much lower than that of the aggregate output in China while the US has the opposite result. That we find employment to be more responsive to output changes in industries whose firm-size distribution is more skewed towards smaller firms needs not be inconsistent with the evidence that larger firms are more cyclically sensitive than smaller ones for a given industry distribution. A aggregate demand only.
We find that an increase in the employment ratio in agriculture from 2 to 30 percent in our model increases fluctuations in aggregate output by almost 40 percent.
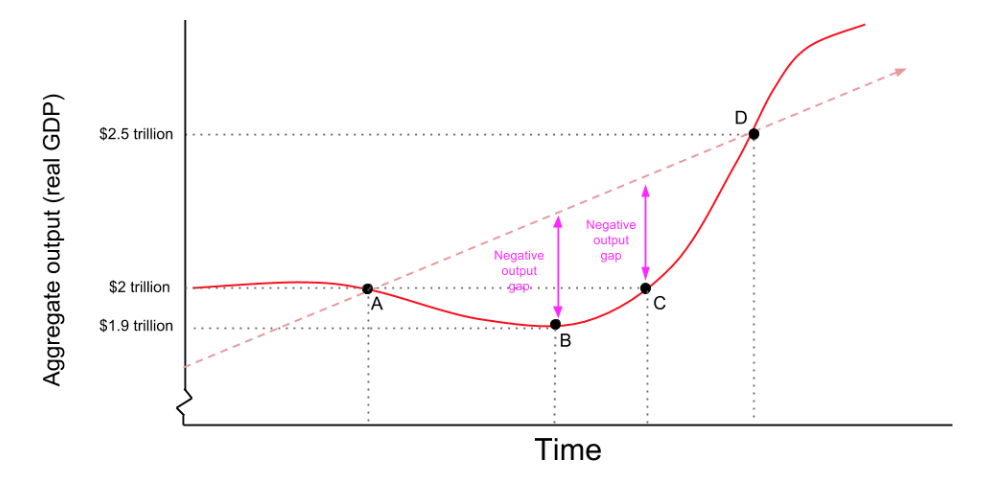
Lesson Summary Business Cycles Article Khan Academy

Solved 6 Real Business Cycle Theory Real Business Cycle Chegg Com
No comments for "Fluctuations in Employment and Output Result From Changes in"
Post a Comment